
STARBUCKS
Starbucks Corporation is an American multinational chain of coffeehouses and roastery reserves headquartered in Seattle, Washington. It was founded in 1971, and is currently the world’s largest coffeehouse chain. As of November 2022, the company had 35,711 stores in 80 countries, 15,873 of which were located in the United States. Of Starbucks’ U.S.-based stores, over 8,900 are company-operated, while the remainder are licensed. The rise of the second wave of coffee culture is generally attributed to Starbucks, which introduced a wider variety of coffee experiences. Starbucks serves hot and cold drinks, whole-bean coffee, micro-ground instant coffee, espresso, caffe latte, full and loose-leaf teas, juices, Frappuccino beverages, pastries, and snacks. Some offerings are seasonal or specific to the locality of the store. Depending on the country, most locations provide free Wi-Fi Internet access.
The idea: Starbucks, founded in 1971 had a mission to become a “third place” to go, to provide a relaxing environment and experience for its customers. One barista decided to start writing the names of customers on cups. The result: The idea was shared with the corporate office. Months later, this ‘first-name’ approach became a standard at every Starbucks store. The company has since launched designated advertising efforts to promote this personalized touch. Today, this ‘first-name’ approach is used four billion times a year at 30,000 locations globally.
LEAN PRODUCT MANAGEMENT BY G.COHEN
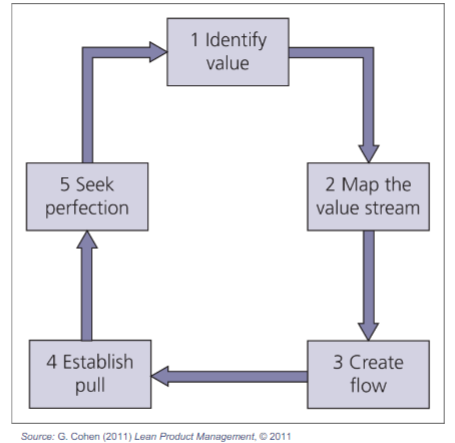
Identify Value
For Starbucks, the value lies in providing high-quality coffee and a unique customer experience. Value is also created through personalized service, convenient locations, and a welcoming atmosphere where customers can relax or work.
Map the Value Stream
Starbucks can map its value stream by analyzing the entire journey of its products, from sourcing coffee beans to serving customers in-store. This involves understanding every step involved in delivering value to customers, including procurement, roasting, distribution, store operations, and customer interactions.
Create Flow
Creating flow at Starbucks involves optimizing processes to ensure a smooth and efficient experience for customers and employees. This could include streamlining the order-taking process, optimizing inventory management to reduce stockouts, and minimizing wait times during peak hours.
Establish Pull
Starbucks can establish pull by aligning production and inventory levels with customer demand. This involves implementing systems to replenish supplies based on actual sales data and customer orders, rather than relying on forecasts or arbitrary production schedules.
Seek Perfection
Perfection, in the context of Starbucks, means continuously striving to improve every aspect of the business to better serve customers and eliminate waste. This could involve ongoing training for baristas to improve service quality, refining store layouts for better traffic flow, and experimenting with new technologies to enhance the customer experience.
ADAPTED FROM SLACK N. ET EL (2004) PEARSON
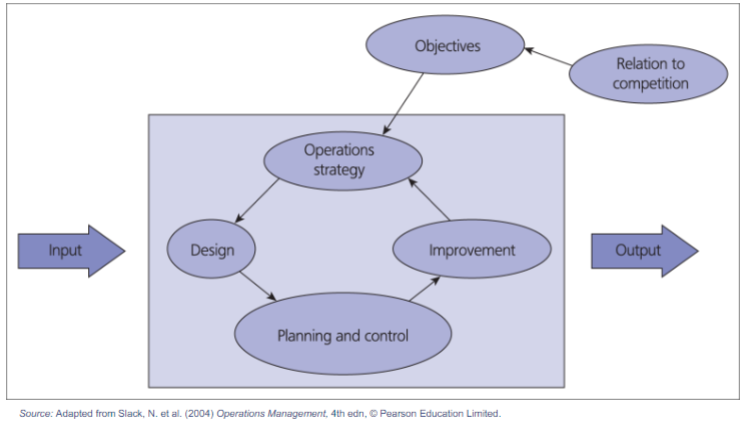
DESIGN
Product Design: Starbucks prioritizes the design of their beverages and food items, aligning them with customer preferences and market trends. For instance, seasonal offerings like the Pumpkin Spice Latte are crafted to draw in customers and generate excitement.
Service Design: Starbucks meticulously plans the ambiance and layout of its stores to establish a warm and inviting atmosphere. This involves careful considerations such as furniture arrangement, lighting, and music selection, all aimed at enhancing the overall customer experience.
PLANNING AND CONTROL
Demand Forecasting: Starbucks employs advanced demand forecasting methods to accurately predict customer needs. By doing so, they can maintain optimal inventory levels and staffing to effectively meet demand, minimizing both stockouts and overstaffing issues.
OPERATION STRATEGY
Quality Focus: Starbucks’ operations strategy is closely integrated with its business strategy, placing significant emphasis on delivering high-quality products and exceptional customer service.
Innovation: A core element of their operations strategy involves ongoing innovation in both product offerings and service approaches, such as the introduction of mobile ordering systems.
IMPROVEMENT
Lean Principles: Starbucks applies lean principles to reduce waste and enhance efficiency throughout its operations. This involves optimizing store layouts and streamlining processes to improve overall effectiveness.
Feedback Mechanisms: Starbucks regularly collects and analyzes customer feedback to pinpoint areas for enhancement and enact necessary adjustments, ensuring continuous improvement in its offerings and services.
OBJECTIVES
Quality: Starbucks prioritizes upholding high standards in both its products and services as a fundamental goal.
Flexibility: The capability to swiftly introduce new products and adapt to shifts in the market. Speed: Ensuring prompt and efficient service delivery, particularly through innovations like mobile ordering and drive-thrus.
RELATION TO COMPETITION
Brand Differentiation: Starbucks sets itself apart from competitors by offering premium products and delivering a distinctive customer experience.
Market Positioning: Strategic placement of stores, consistent delivery of quality products, and a robust brand identity collectively give Starbucks a competitive advantage in the market.
REFERENCES
Haskova, K. (2015). Starbucks marketing analysis. CRIS-Bulletin of the Centre for Research and Interdisciplinary Study, 1(11), 11-29.
