
One key strategy for successful upskilling at PwC is citizen-led innovation. Here’s how it works. Business leaders play a crucial role in setting the direction, goals, and providing the necessary training, tools, and resources for employees to learn and apply new skills effectively. Employees are empowered to take the lead in innovating, building, sharing, and test-driving solutions without being mandated or restricted. They have the freedom to choose their learning methods and level of participation, which fosters a sense of ownership and motivation. Through the application of new skills and digital assets, employees can automate manual tasks, leading to significant time savings and quality improvements by eliminating human error. The approach generates emotional commitment among employees as they see more purpose in learning new skills and contributing to the organization’s success. This emotional investment drives engagement and enthusiasm for continuous learning and improvement. Upskilling is not just about preparing for future roles but also about helping employees grow within their current roles by becoming infinite learners. This approach empowers employees to actively participate in their learning and apply new digital skills to their work. It emphasizes leadership support, employee autonomy, and incentives to encourage participation. By allowing employees to contribute to innovation and problem-solving within the organization while continuously learning and adapting to changing work environments, PwC fosters a culture of innovation and growth.
PwC’s own experience with citizen-led upskilling initiatives serves as a model for other companies. The company provides employees with the freedom to opt into upskilling opportunities and actively participate in innovation efforts. This approach has yielded significant results, including improved efficiency (the automation of 6.5 million hours of manual tasks), quality (7,000 contributions to our Digital Lab), and employee engagement (55,000 PwC employees in the US have been upskilled and regularly use Digital Lab).
PwC’s approach to upskilling and innovation through the Digital Lab and citizen-led initiatives aligns well with the principles of intrapreneurship. It creates an environment where employees are motivated and empowered to drive change and contribute to the company’s growth and success

PWC
CITIZEN-LED INNOVATION
In 2019, amidst the context of pandemic recovery, acknowledging the potential economic advantages of proficient upskilling initiatives, PwC underscores the necessity for organizations to prioritize the enhancement of their workforce’s digital skills. This commitment is exemplified through Digital Lab – a collaborative platform where individuals actively crowdsource and disseminate their personally developed solutions, encompassing bots, data models, and automated workflows.
PwC’s own experience with citizen-led upskilling initiatives serves as a model for other companies. The company provides employees with the freedom to opt into upskilling opportunities and actively participate in innovation efforts. This approach has yielded significant results, including improved efficiency (the automation of 6.5 million hours of manual tasks), quality (7,000 contributions to our Digital Lab), and employee engagement (55,000 PwC employees in the US have been upskilled and regularly use Digital Lab).

Crowdsourcing
In the case of PwC’s Digital Lab, the platform acts as a crowdsourcing tool where employees contribute and share their digital solutions. This collaborative environment supports intrapreneurs who are developing new automated workflows, bots, and data models. Employees who actively participate in crowdsourcing initiatives can emerge as intrapreneurs, taking the lead on projects that originate from collective contributions. This interconnected approach enhances both the quality and quantity of innovations within the company.
Innovation Dilemma
Efficiency Gains, Creativity Gains
Ambidexterity

Through this approach, PwC makes an effort to address the innovation dilemma, balancing between efficiency and creativity.
On the one hand, PwC’s upskilling strategy aims to improve the efficiency of its workforce by providing targeted training and resources to employees, enabling them to perform tasks more effectively. By leveraging automation and digital tools learned through upskilling, employees can streamline processes and reduce manual workload, resulting in significant time savings. The emphasis on employee autonomy and empowerment encourages individuals to proactively identify and implement efficiency improvements in their day-to-day work.
On the other hand, the citizen-led innovation approach fosters a culture of creativity and innovation within the organization, allowing employees to contribute their ideas and solutions to address business challenges. Employees are encouraged to experiment with new technologies and techniques, leading to the development of innovative digital solutions tailored to specific business needs. The freedom to opt in and participate in upskilling activities enables individuals to enhance their creativity and problem-solving skills, driving continuous improvement and innovation across the organization.
By investing in upskilling initiatives like the Digital Lab, PwC explores new opportunities for innovation and growth in the digital space. At the same time, PwC continues to exploit its existing resources and capabilities by leveraging the skills and expertise of its workforce. Instead of neglecting their current strengths, PwC uses them as a foundation for further innovation and development.
Managing Organization Knowledge – Absorptive Capacity
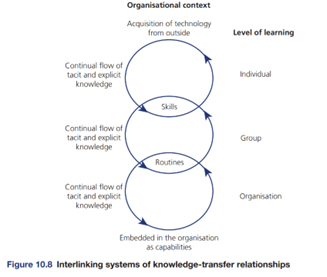
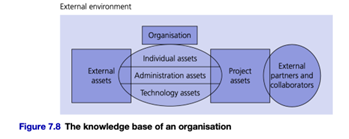
Moreover, PwC’s strategic approach to upskilling and citizen-led innovation can indeed be seen as a way to manage individual-level knowledge and assets (Figure 7.8 and 10.8). By investing in their employees’ skills and creating a receptive environment for innovation, PwC enhances its absorptive capacity, making it well-prepared to acquire and leverage technology from outside sources. This approach reflects a proactive stance towards organizational learning and adaptation, which is essential for staying competitive in a rapidly changing business landscape.
Academic article
O’reilly Iii, C. A., & Tushman, M. L. (2008). Ambidexterity as a dynamic capability: Resolving the innovator’s dilemma. Research in organizational behavior, 28, 185-206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riob.2008.06.002

In the context of the post-pandemic period, PwC’s approach seems to be a wise strategy for navigating uncertainty and embracing change. By embracing ambidexterity as a dynamic capability, as highlighted by O’reilly III & Tushman (2008), PwC has demonstrated its ability to simultaneously explore new opportunities and exploit existing strengths, ensuring its resilience and adaptability in a rapidly evolving landscape. Ambidexterity serves as a critical mechanism for organizational adaptation, providing invaluable insight into the process through which organizations evolve. In essence, PwC’s embrace of ambidexterity not only positions it for success in the face of ongoing challenges but also underscores the importance of agility and innovation in today’s dynamic business environment.
references
Trott, P. (2021). Innovation Management & New Product Development (7th edition)
